1 Which of the Following Describes a Titration Curve
The volume of titrant which reacts with the analyte is known as titre volume. Which of the following would help you identify a titration curve that involved a strong acid titrated by a weak base.
21 19 Titration Curves Chemistry Libretexts
Which of the following equations is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.

. As the solution nears the point where all of the H are neutralized the pH rises sharply and then levels out again as the solution becomes more basic as more OH- ions are added. It is a quantitative method of chemical analysis. The pH at the equivalence point is always equal to 7.
Note that D is the equivalence point. If the pH is above 7 the analyte is either a weak or strong base. 4 stages in a titration.
II The pH change is slow until near the equivalence point. PH A HF D B HF and OH C OH B D F mL OH- Which of. The first marker is if the initial pH is above or below 7.
Standard being added 3. III At the equivalence point pH changes by a large value. The following combinations produce.
Standard added in excess. Check all that apply. Important features of titration curves for strong acids and bases.
Although you normally run the acid from a burette into the alkali in a flask you may need to know about the titration curve for adding it the other way. Select all that apply The curve for the weak acid-strong base titration rises gradually through a buffer region before the steep rise to the equivalence point. NAWhich of the following describes the following titration curve.
Titration curve A plot of pH Vs millilitres of titrant showing the manner in which pH changes Vs millilitres of titrant during an acid-base titration. NAWhich of the following describes the following titration curve. AThe pH at the equivalence point is lower than 7.
Gradual increase of pH until past the midpoint. I The beginning pH is low. AP Chemistry-Titration Graphs Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
IV Beyond the equivalence point pH rises rapidly. The pH of the solution at the equivalence point depends on the characteristics of the analyte and the titrant. PH log695 10 5 4158.
2 The pH of the solution at equivalence point is dependent on the strength of the acid and strength of the base used in the titration. The initial pH is typically low and can be determined knowing the concentration of the strong acid. 1 The equivalence point of an acid-base reaction the point at which the amounts of acid and of base are just sufficient to cause complete neutralization.
Is HF option A is correct because it is titration begi. Describe the preparation for each of the following solution showing all relevant calculations answers rounded to 4 decimal places. NCERT P Bahadur IIT-JEE Previous Year Narendra Awasthi MS Chauhan.
100 54 ratings 1 first curve point A. BThe pH at the equivalence point is higher than 7. All acid titration curves follow the same basic shapes.
In this a titrant of known concentration is prepared and used to react with the analyte to determine its concentration. There is a steep climb in pH before the first midpoint. Right before the equivalence point there is a sharp increase in pH.
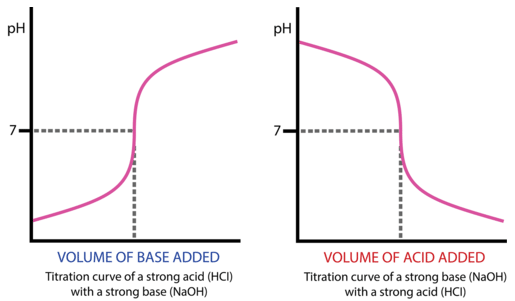
Which of the following statements correctly describe a typical titration curve for the titration of a strong acid by a strong base. The following titration curve could describe which of the following peptides. In the beginning the solution has a low pH and climbs as the strong base is added.
The key features of a curve to indicate titration of a weak diprotic acid by KOH of equivalent strength. 1 hydrochloric acid HClaq with sodium hydroxide NaOHaq. Which of the following options correctly describe the differences between the titration curve for a weak acid-strong base titration and a strong acid-strong base titration.
Titrand The titrand is any solution to which the titrant is added and which contains the ion or species being determined. The slope of the pH curve increases slowly until very close to the equivalence point. Acid-base titration the most frequently employed method of titration adheres to certain curve trends established by the acid and the base involved.
Equivalence Stoichiometric Point reached 4. View the full answer. In simple terms the titration curve is the plot of pH of the analyte titrand versus the volume of the titrant added as the titration progresses.
You will obtain titration curves for the following combinations of acids and bases exact concentrations will be labeled on the reagent bottles and should be written in your data table. 2 acetic acid CH 3 COOHaq with sodium hydroxide NaOHaq. Solution for Consider the following titration curve of a 0200 M weak monoprotic acid HA solution with 0160 M NaOH.
PH of sample before any standard is added 2. 250 mL of 2000 M HNO 3 from a concentrated solution that is 68 m v HNO 3 and has a specific gravity of 141. The recorded volume and pH values will generate titration.
PH 10 85 35 1 2 3 Eq OH- O a. Up to 24 cash back 1 418 Comparing the Shapes of Titration Curves and Choosing Indicators Titration of a Strong Acid with a Strong Base Titration of a Weak Acid with a Strong Base Recall. Comparing the titration curves for HCl and acetic acid in Figure 1743a we see that adding the same amount 500 mL of 0200 M NaOH to 50 mL of a 0100 M solution of both acids causes a much smaller pH change for HCl from 100 to 114 than for acetic acid 288 to 416.
NCERT DC Pandey Sunil Batra HC Verma Pradeep Errorless. All the following titration curves are based on both acid and alkali having a concentration of 1 mol dm-3In each case you start with 25 cm 3 of one of the solutions in the flask and the other one in a burette. For the preparation of a titration curve of an acid-base titration the base is added in small increments and the pH of the acid in each step is determined with a pH meter.
Titration or volumetric analysis is a method used in the laboratory to determine the concentration of an unknown solution. The curve starts at a higher pH than a titration curve of a strong base. Two key markers in a titration curve help us identify whether the analyte and titrant in a titration is a strong or weak acid or base.
Which of the following accurately describes the primary species in solution at point A on the titration curve for the titration of HF with NaOH.

Titration Curves Equivalence Point Article Khan Academy


No comments for "1 Which of the Following Describes a Titration Curve"
Post a Comment